POI Data - Definition
POI Data, or Point of Interest Data, is a large amount of specific and important information about certain noteworthy points of interest in provided or chosen geographic areas. It covers broad categories of interest areas that go from the leisure ones like parks and museums or art galleries, to others more vital and practical such as hospitals, schools, and supermarkets.
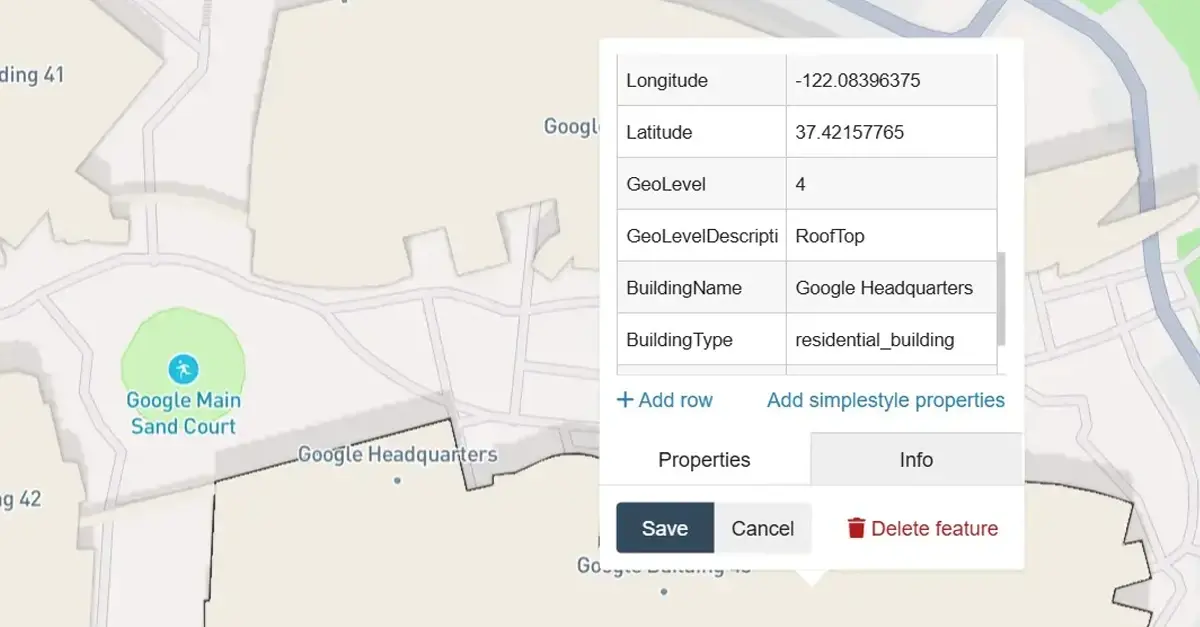
Every point can contain parameters such as the name of the point, geographic coordinates–latitude and longitude, category, and metadata regarding operations, opening hours, contact information and customers’ reviews. Such information assists users, commercial enterprises, and particular systems in defining and identifying areas of interest without errors.
POI Data has features that can be used in traveling, city mapping, supply chain, and promotion. For instance, a food delivery app uses POI Data to direct drivers to the restaurants and clients’ locations. Companies especially rely on POI Data to identify customer demand, analyze the market, and make corresponding business decisions.
POI Data is created by thousands, or millions of points of interest collected globally.
What is a Single Point of Interest?
A single Point of interest (POI) means a special point that has a unique importance for users or businesses. A single POI is allotted basic parameters, which are name, and geographic coordinates, and may contain features such as type of service and access.
For example, single points of interest are easy to identify on a tourist map: a museum–its opening hours, ticket prices, user feedback, etc. Companies often calculate the importance of a single POI to work out its significance, customers’ attendance, and potential to influence marketing or operational fields. In several industries, a single POI is the data element that goes into the construction of larger datasets.
Example of a Point of Interest
- POI A landmark on a digital map

- POI A shopping mall on a digital map

What Belongs to POI Data, and What Is POI Data?
POI Data implies a vast amount of information related to essential points of interest, that is presented in the dataset, in various ways. Such datasets comprise the geographic coordinates, the names of the points of interest, categories, and all other data, creating a profile for every location.
What Belongs to POI Data?
POI Data includes:
- Core Details: Name, identifiers, contact details, opening hours, industry and address information.
- Geographic Coordinates: Geographical coordinates (lat/long)
- Categorization: Classification into the retail trade and accommodation services and other categories and subcategories.
- Metadata: Open hours, ratings, reviews, and facilities for the disabled.
Detailed Overview
POI Data can be static or dynamic:
- Static Data: Attributes that remain constant throughout the period, which may include place, type of business, and name, respectively.
- Dynamic Data: Dynamic information, such as availability or traffic density, hours of service, etc.
This data is useful in almost all sectors of the economy. For example, delivery companies need point-of-interest data to plan their routes, and city planners use it to determine areas that need the installation of parks and transport, city infrastructure, etc.
Like other data, POI Data also helps in real-time decision-making. Consumer patterns, such as tracking footsteps or identifying hot fixations in a given area, are perceived as ways in which businesses can study consumer behavior patterns.
How Are Points of Interest Divided?
Interest points or POIs are grouped in that they are classified depending on their function, usefulness, or business type. Classification helps other businesses or even applications to index, sort, analyze, and put into practice information about POI in the best way for them.
Primary Categories
- Business to Business: Machinery, industrial products, utilities, telecommunication, and transportation.
- Hospitality and Tourism: Accommodation–Hotels and restaurants, art institutions–museums and landmarks.
- Business Premises–educational facilities, health facilities, and bureaucracies.
- Leisure–Parks, gyms, and all other places people may go to relax, such as theaters.
- Transportation: These areas include airports, train stations, and parking lots.
Subcategories
For analysis, each primary category is split into subcategories that provide more refined insight into practices. For instance, “retail” means supermarkets, clothing, or electronic shops. Likewise, “restaurants” can be sub-classified as fast foods, elegant restaurants, and cafeterias.
What is POI in Business?
Point of Interest (POI) in business defines any location that can be of strategic, operational, or marketing significance. Businesses use POI data for understanding the trends occurring in geography, strategizing their operations, and optimizing clients’ experience.
For instance, a retailer may apply POI data in assessing store sites regarding foot traffic around the area, and the density of other similar retailers and the buying public around the area. In the same way, marketing agencies employ the usage of POI data in geo-targeted campaigns which release promos to users near points such as malls or events.
POI data is also used in the logistics industry, in which firms design delivery routes and siting of warehouses utilizing accurate POI information. In addition to a working tool, POI data is utilizable for various decisions, for instance, to determine the areas where the number of points of interest is insufficient or to assess the effectiveness of particular branches.
Businesses use POI data mostly through geosocial networking applications, physical POI terminals, as well as through mobile applications from businesses themselves.
POI data can be used in a myriad of ways to optimize the effectiveness of a business, improve decision outcomes, and even improve the services being offered to consumers.
How Businesses Use POI Data?
- Market Research and Expansion
The analysis shows that businesses planning to expand their operations should consider the use of POI data. Using the information on popular facilities, locations of competitors, and customers’ preferences, such as areas with high traffic intensity, businesses can identify the most appropriate locations for new outlets or services. For instance, a retail furniture chain store might evaluate ways of measuring the demographic density of populations residing on adjacent premises, the availability of parking lots, and other compatible businesses to determine the store location. - Geo-Targeted Marketing
POI data is utilized by companies to develop marketing promotions that are targeted by location. In this way, using information on which sites their target audience is likely to be frequent, they can post suitable advertisements or special offers. For instance, a coffee-providing chain can use POI data to promote mobile coupons for two cups in the morning near their shops. This kind of marketing enhances customer relations and thus increases the sales of the products. - Transportation and Supply Chain Management
In an additional role, their data, the so-called POI, is important for logistical processes. A location such as FedEx, which delivers packages, needs POI data to navigate the most efficient route while another, like Uber, an online car service provider, also needs POI data. This also eliminates fuel expenditure and guarantees on-time delivery to the customers. In warehouses, POI data is applied to determine the most appropriate strategic locations for warehouse distribution, as they are near suppliers' and customers’ concentration areas. - Customer Behavior Insights
In this analysis, businesses can gain insight into their customers and the POI data. By thus recognizing often visited places or places with high attendance rates, business entities can adjust their portfolios. For example, because of points of interest, a fitness application can suggest nearby gym facilities or parks. - Urban Planning and Development
Governments and every business engaged in the planning of cities to evaluate physical requirements use POI data. For instance, they might use POI data to determine which areas are not well developed, specifically areas without schools, hospitals, or other recreational facilities; information they could use to allocate future development projects. - Competitor Analysis
Competitive analysis is one of the most relevant fields in which businesses apply POI data. For instance, a restaurant business might look at the access of its competitor restaurants in order to determine the level of competition and service delivery gaps that might be fit for its services.
How Businesses Get POI Data?
- Professional Point of Interest Data Providers
Point of Interest Services providers of data such as InfobelPro present relevant, reliable, and up-to-date POI data depending on business requirements. Such providers feature geometric coordinates, subcategories, and functional metadata, thus guaranteeing that companies get useful information. Most such services can be tailored to categorize and sort results; this is valuable if a business is interested in data from a particular sector. - Application Program Interfaces (APIs)
It often occurs that companies employ APIs to incorporate real-time POI data into their environments. For instance, any firm that is in the business of producing navigation applications or ride-hailing applications needs dynamic and accurate data that is provided by POI APIs. These APIs offer real-time data, making the delivered data current and useful. - Open Data Sources
Some POI data is proven to be available for free by using OpenStreetMap, an official database, or other social projects. Although these sources of information may be cheap to acquire, they may not be as accurate or comprehensive, or up-to-date as a business needs. It has become apparent that open data is preferable for minor usage or when data is not monetized. - Custom Data Collection
Some form a larger enterprise that captures POI data through surveys, geolocation applications, or smart RFID tags. This way, the data collected is exceptionally relevant to their operations because it is collected from specific groups of people who have a direct link to their business. But it calls for a lot of effort and is an area of high competence. - Third-Party Marketplaces
The data can also be purchased from third-party marketplaces dealing with point-of-interest data. These services provide the organizations with the selected sets of datasets by offering them collections of datasets from multiple providers.
For a detailed overview, visit our guide: 9 Best POI Data Providers.
Common Use Cases of POI Data
Businesses and developers find POI Data valuable since it has numerous uses across every establishment’s sectors.
Examples of POI Data Usage
- Retail Store Location
A supermarket chain applies POI data in assessing the feasibility of a store location, in that it should be near POIs and there should be limited rivalry. - Ride-Sharing
Companies like Uber operate based on POI data to enhance the locations where customers are picked up and dropped off. - Healthcare Access
POI data is useful in establishing areas that require clinics, pharmacies or hospitals by identifying areas that lack such facilities. - Tourism Apps
Tourism apps provide recommendations to restaurants, attractions, or hotels, taking into consideration data on POI and user preferences.
Such practical uses demonstrate the usefulness of POI data in improving the productivity and satisfaction of users.
Challenges of POI Data
- Data Accuracy
POI data that is outdated or missing information can create wrong decisions and service delivery. - Coverage Gaps
They apply well only to a limited extent because current POI data are not exhaustive in rural settings. - Standardization Issues
The differences in data formats compound the problem of integration among providers.
To counter these challenges, working with reliable data suppliers and updating the data more often is necessary.
Advantages of POI Data
- Improved Decision-Making
It improves the formulation of business development strategies. - Enhanced Customer Engagement
It makes the provision of services relevant to the geographical location and increases the customer satisfaction level. - Operational Efficiency
The affordable and timely delivery of products enhances efficient operations.
Final Thoughts
POI data is crucial for companies that would like to remain relevant and sensitive to changes in the environment. With the help of High-quality data and tools, the firms can find new growth opportunities, improve organizational performance, and provide an excellent customer experience.





Comments